Weight-loss surgery, also called bariatric surgery, is the treatment option today that may help treat obesity in people when diet, exercise and medication have failed. In addition to treating obesity, these surgeries are effective in treating diabetes, high blood pressure, sleep apnea and high cholesterol, among many other diseases. These operations can also prevent future health problems. The benefits allow patients with obesity who undergo treatment to enjoy a better quality of life and a longer lifespan.
Candidates for bariatric surgery
Bariatric surgery is typically recommended for adults with a body mass index (BMI) of 40 or greater. If you have other serious health conditions, such as diabetes or heart disease, bariatric surgery may be beneficial if your BMI is between 35 and 40.
Bailey Bariatrics offers a variety of approaches to bariatric surgery, but all procedures either change the way the digestive system works, or physically reduce the size of the stomach so it holds less food. Some procedures are a combination of both practices.
Gastric bypass (Roux-en-Y)
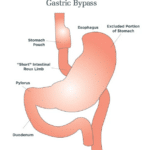
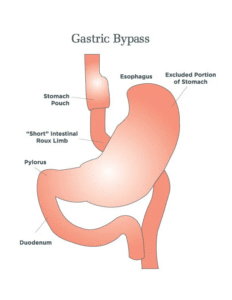
The Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, often called the “gastric bypass,” has been performed for more than 50 years and the laparoscopic approach has been redefined since 1993. It is one of the most common operations and is very effective in treating obesity and obesity related diseases. The name is a French term meaning “in the form of a Y.”
Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy
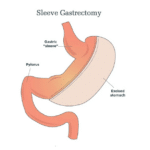
The laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy, often called the “sleeve,” is performed by removing approximately 80% of the stomach. The remaining stomach is the size and shape of a banana.
Single Anastomosis Duodenal-Ileal Bypass with Sleeve Gastrectomy (SADI-S)

The SADI-S operation starts the same way as the sleeve gastrectomy, making a smaller tube-shaped stomach.
It’s important to carefully consider making this significant change in your life. Bariatric surgery requires committing to a healthy lifestyle for a lifetime. Ask your doctor for their opinion on your treatment options, and if bariatric surgery is right for you.
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass
The Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, often called gastric bypass, has been performed for more than 50 years. It is one of the most common operations and is very effective in treating obesity and obesity-related diseases. The name is a French term meaning “in the form of a Y.”
The Procedure
Gastric bypass surgery starts with the stomach being divided into a smaller top portion (pouch), which is about the size of an egg. The larger part of the stomach is bypassed and no longer stores or digests food.
The small intestine is also divided and connected to the new stomach pouch to allow food to pass. The small bowel segment, which empties the bypassed or larger stomach is connected into the small bowel approximately three to four feet downstream, resulting in a bowel connection resembling the letter Y.
Eventually, the stomach acids and digestive enzymes from the bypassed stomach and first portion of the small intestine will mix with food that is eaten.
How it works
Like many bariatric surgeries, the newly created stomach pouch is smaller and able to hold less food, which means fewer calories are ingested. Additionally, the food does not meet the first portion of the small bowel, and this results in decreased absorption. The modification of the food course through the gastrointestinal tract can decrease hunger, increase fullness, and allow the body to reach and maintain a healthy weight.
The impact on hormones and metabolic health often results in the improvement of adult-onset diabetes even before any weight loss occurs. The operation also helps patients with reflux (heartburn) and often the symptoms quickly improve. Along with making appropriate food choices, patients should avoid tobacco products and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen and naproxen.
(Click on photo to enlarge)
Is it right for me?
Advantages
- Reliable and long-lasting weight loss
- Effective for remission of obesity-associated conditions
- May help improve quality of life by reducing physical limitations, increasing mobility and improving self-esteem and body image
- May have positive impact on metabolic health
- Refined and standardized technique
Disadvantages
May cause “dumping syndrome”, a feeling of sickness after eating or drinking, especially sweets
Technically more complex when compared to sleeve gastrectomy or gastric band
More vitamin and mineral deficiencies than sleeve gastrectomy or gastric banding
Risk of small bowel complications and obstruction
Risk of developing ulcers, especially with NSAID or tobacco use
Watch the video below to learn more about Roux-en-Y gastric bypass.
Patient testimonials
Click these links to read testimonials from patients who have undergone gastric bypass procedures at Bailey Bariatrics:
Sleeve Gastrectomy
The laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy, often called the “sleeve,” is performed by removing approximately 80% of the stomach. The remaining stomach is the size and shape of a banana.
The procedure
The stomach is freed from organs around it, then surgical staplers are used to remove 80% of the stomach, making it much smaller.
How it works
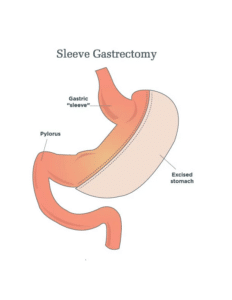
The new, smaller stomach holds less food and liquid helping reduce the amount of food (and calories) that is consumed. By removing the portion of the stomach that produces most of the “hunger hormone,” the surgery influences the metabolism. It decreases hunger, increases fullness, and allows the body to reach and maintain a healthy weight as well as control blood sugar. The simple nature of the operation makes it very safe without the potential complications from surgery on the small intestine.
(Click on photo to enlarge)
Is it right for me?
Advantages
- Technically simple and shorter surgery time
- Can be performed in certain patients with high-risk medical conditions
- May be performed as the first step for patients with severe obesity
- May be used as a bridge to gastric bypass or SADI-S procedures
- Effective weight loss and improvement of obesity-related conditions
- May help improve quality of life by reducing physical limitations, increasing mobility and improving self-esteem and body image
- May help reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety
Disadvantages
- Less impact on metabolism compared to bypass procedures
- Non-reversible procedure
- May worsen or cause new onset reflux and heart burn
Watch the video below to learn more about Sleeve Gastrectomy.
Patient testimonials
Click these links to read testimonials from patients who have undergone laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy procedures at Bailey Bariatrics:
SADI-S
The Single Anastomosis Duodenal-Ileal Bypass with Sleeve Gastrectomy, referred to as the SADI-S or Loop Duodenal Switch, is the newest procedure to be endorsed by the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS).
The procedure
The surgery starts the same way as the sleeve gastrectomy, making a smaller tube-shaped stomach. The first part of the small intestine is divided just after the stomach. A loop of the intestine is measured several feet from its end and is then connected to the stomach. This is the only intestinal connection performed in this procedure.
How it works
When the patient eats, food goes through the pouch and directly into the latter portion of the small intestine. The food then mixes with digestive juices from the first part of the small intestine. This allows enough absorption of vitamins and minerals to maintain healthy levels of nutrition. This surgery offers weight loss along with less hunger, more fullness, blood sugar control and diabetes improvement.
(click photo to enlarge)
Is it right for me?
Advantages
- Highly effective for long-term weight loss and reduced risk of obesity-related health conditions
- Simpler and faster to perform (one intestinal connection) than gastric bypass or BPD-DS
- May result in improved metabolic health
- Excellent option for a patient who already had a sleeve gastrectomy and is seeking further weight loss
Disadvantages
- Risk of looser and more frequent bowel movements
- Vitamins and minerals are not absorbed as well as in the sleeve gastrectomy or gastric band
- Newer operation with only short-term outcome data
- Potential to worsen or develop new-onset reflux
Watch the video below to learn more about SADI-S.